Difference between revisions of "Reinit"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Reinit.png|thumb|alt=Reinit|Reinit]] | |||
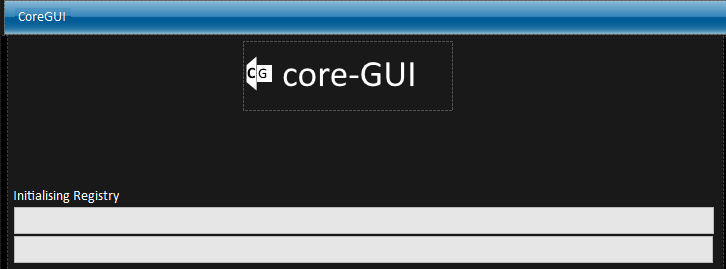
[[Reinit]] is responsible for creating and maintaining [[CoreGUI's Virtual Registry Filesystem]] when CoreGUI starts. | [[Reinit]] is responsible for creating and maintaining [[CoreGUI's Virtual Registry Filesystem]] when CoreGUI starts. | ||
During a standard CoreGUI startup, [[F1]] will call [[Reinit]] after [[bstrap]] has finished. [[initsetup]] is also present during | During a standard CoreGUI startup, [[F1]] will call [[Reinit]] after [[bstrap]] has finished. [[initsetup]] is also present during | ||
this process to report the startup progress. | this process to report the startup progress. | ||
[[Reinit]] is a slightly more advanced version of [[Reginit]] as it automatically configures the environment at startup | |||
and fills missing values for applications automatically. | |||
== Trivia == | == Trivia == | ||
Revision as of 01:19, 19 August 2021
Reinit is responsible for creating and maintaining CoreGUI's Virtual Registry Filesystem when CoreGUI starts.
During a standard CoreGUI startup, F1 will call Reinit after bstrap has finished. initsetup is also present during this process to report the startup progress.
Reinit is a slightly more advanced version of Reginit as it automatically configures the environment at startup and fills missing values for applications automatically.
Trivia
- On Enterprise editions of CoreGUI, the top bar is blue, in standard versions, this is black.
- Reinit originally had one progress bar, however a second was added for reinit application initialisation.
- Reinit is one of the few CoreGUI System Applications to have no user-interactable functions.
- Reinit does not display as Reinit, and instead displays it's title as CoreGUI.
- Reinit stands for 'Registry Initialisation'.