Difference between revisions of "Vmdetect"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Trivia == | == Trivia == | ||
* [[Vmdetect|VMDetect]] is one of few dialog boxes to use [[F1]]'s [[appopacit]] | |||
* [[Vmdetect|VMDetect]] shows as "VM Detect x86" | * [[Vmdetect|VMDetect]] shows as "VM Detect x86" | ||
* [[Vmdetect|VMDetect]] has the error icon ([[noentry]]) as it's dock icon | * [[Vmdetect|VMDetect]] has the error icon ([[noentry]]) as it's dock icon | ||
Latest revision as of 18:16, 15 August 2021
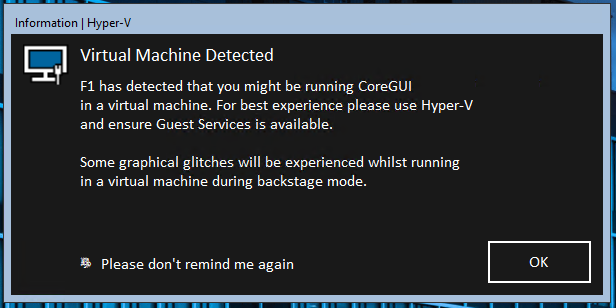
VMDetect is part of the initial F1 startup process and is responsible for detecting if the CoreGUI Instance is running under a Hypervisor or is a Virtual Machine.
VMDetect cannot be launched manually, however the dialog box can be made present again if disabled and running under a virtual machine.
- By modifying the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\CoreGUI\inf, setting disVM to 0 (Enterprise Versions only)
- By deleting the file C:\CGUI\disVM.cgui
Trivia
- VMDetect is one of few dialog boxes to use F1's appopacit
- VMDetect shows as "VM Detect x86"
- VMDetect has the error icon (noentry) as it's dock icon
- VMDetect has the warning icon as it's windows taskbar icon
- VMDetect uses the networkconnected resource
- A deprecated function called vmdetect-gui was originally introduced to detect hypervisors but was never implemented into F1
- VMDetect's file name is actually called vboxwarning